. Introduction
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is one of the three major food crops in the world, providing security for more than 50% of the world’s population, and is also the crop with the largest water demand, accounting for about 70% of the total agricultural water demand (Luo, 2010; Q. F. Zhang et al., 2008). Climate change, population growth and the reduction of arable land have had an adverse impact on crop yield and food production (A. Wang et al., 2013; X. Zhang et al., 2017). Therefore, how to improve rice yield to cope with the challenges of growing food demand is an important goal of current rice breeding (Abberton et al., 2016; Kissoudis et al., 2016; Yin et al., 2020).
The main factors that determine the yield of rice include effective panicle number, grain number per panicle and 1,000-grain weight. It is particularly important to clarify the molecular mechanisms of yield traits, which are the basis for the cultivation of high-yield rice varieties (J. Chen et al., 2015; L. Chen et al., 2023; Huang et al., 2022). Currently, many main QTLs/genes have been cloned and verified to be in control of rice yield traits. For example, OsGA20ox1 is one of the major cloned QTL controlling rice yield, and inhibition of the expression of OsGA20ox1 and OsGA20ox2 reduces the height of rice plants. Further studies showed that it can induce the accumulation of cytokinin and gibberellin and activate the expression of genes related to panicle development to affect the number of grains and the yield (Su et al., 2021; Y. Wu et al., 2016). OsDPE2 is characterized as a cytoplasmic dismutase gene. Knockout of this gene significantly reduces the number of panicles and tillers as well as the seed-setting rate (Zheng et al., 2023). The OsCKX2 (Gn1a) gene encodes an enzyme that degrades cytokinin. Weakened expression of this gene increases the accumulation of cytokinin in the inflorescence meristem, the number of reproductive organs and the number of grains per panicle, ultimately improving the yield of rice (Ashikari et al., 2005; Rong et al., 2022).
Plant height is one of the key factors determining plant architecture, which has an important impact on crop yield and is an important trait for breeding rice varieties. Some genes have also been reported to affect plant height, such as OsDEP1, OsTubA2 and FLR2. OsDEP1 is a major QTL that controls rice panicle type, regulating plant type traits, including erect panicles and plant height. Phenotypic analysis of near-isogenic and transgenic lines revealed that the functional allele OsDEP1 caused panicle drooping, while the functional loss mutation OsDEP1 caused panicle erection, thereby affecting plant height (Zhou et al., 2009). OsTubA2, one encoding α microtubulin, a gene that regulates cell elongation independently of the BR signaling pathway, can cause plant dwarfing and affects plant architecture and yield (Segami et al., 2012). FLR2, a homologous gene with Arabidopsis FERONIA (FER), affects cell elongation through the GA synthesis pathway and other phytohormones, thereby regulating plant height (C. Li et al., 2016).
Polyploidization, an important driving force for species formation and evolution, is highly prevalent in nature (Jiao et al., 2011; Peer et al., 2017; Soltis, 2005; Wolfe, 2001). As an important food crop, rice also exhibits the polyploidization phenomenon (R. Chen et al., 2021; Paterson et al., 2004; Wing et al., 2018; Yu et al., 2005). Polyploid rice plants not only have some advantageous agronomic traits, such as greater height and robustness, longer panicles, larger grains and increased yield, but also have enhanced stress resistance and improved seed quality (R. Chen et al., 2021; B. Wu et al., 2018). However, little is known about the mechanisms underlying these changes. In this study, we identified a polyploid rice strain ‘Balilla’ tetraploid (‘Balilla-4x’) synthesized previously that exhibits advantageous agronomic traits and seed quality (N. Wang et al., 2022a). The results indicate that changes in agronomic traits and rice quality may be attributed to altered expression of crucial yield genes. This study provides a basis for using polyploid technology to improve the agronomic traits and nutritional quality of rice and also provides a new theoretical reference for the breeding of high-yield and high-quality rice varieties using polyploid technology.
. Material and methods
Plant materials
The artificially synthesized tetraploid (‘Balilla-4x’, 2n = 4x = 48) results from the doubling of the ‘Balilla’ diploid (‘Balilla-2x’). ‘Balilla-2x’ (O. sativa ssp. japonica, 2n = 2x = 24), a rice variety from Italy with a low seed-setting rate, was provided by the Polyploid Genetics Laboratory of Hubei University, Wuhan, China.
Growth conditions of plant materials
The rice plants (‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’) used in this study grew in the paddy field of experimental fields in Shanghai during the natural growing seasons.
Phenotypic observations of rice
The agronomic traits of ‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’ plants, including plant height, panicle length, tillering number and 1,000-grain weight, were manually measured by Meter ruler (Deli, China) after the plants were harvested. One thousand-grain weight was measured by a precision balance (accuracy 0.1 mg, LC-SFA524, Lichen, China), and the weight of 1,000 seeds was calculated using the formula (seed weight)/(number of seeds) × 1,000. The grain length, width and thickness of dry seeds were determined with Vernier callipers (accuracy ± 0.02 mm) purchased from Syntek in China. The moisture content of seeds was determined using AOAC official method 930.15. Protein content was determined using the Kjeldahl2300 Analyzer. The lipid content was measured using a lipid analyzer (SZF-06A, Nanjing, China). More than 300 plump and insect-free seeds were selected for measurement. At least three biological replicates were used for analyses.
RNA isolation and qPCR
The leaves of ‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’ plants were sampled for RNA isolation. According to the manufacturer’s instructions, total RNA was extracted from rice leaves using TRNzol-A+ reagent (Tiangen, Beijing, China). The reverse transcription of total RNA was achieved using EasyScript One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis Super Mix (TransGen, Beijing, China). Quantitative analysis of gene expression was performed using TransGen’s TransStart®; Top Green qPCR SuperMix kit and Bio-Rad CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, USA). The PCR procedure was as follows: 94 °C 30 sec, 94 °C 5 sec, 55 °C 15 sec, 72 °C 10 sec, 30–35 cycles. The OsActin gene (No. AY212324) was used as the internal reference to calculate the relative expression levels of the target genes (Livak & Schmittgen, 2001).
RNA-Seq and enrichment analysis of DEGs
‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’ plants (three replicates, with at least 30 plants per line) grew for 3–4 weeks. The leaves of these plants were sampled for rice transcriptome sequencing. TRIzol reagent (Life Technologies) was used to extract total RNA, and the concentration of extracted RNA was measured. Qualified RNA samples were then used for library construction according to the Tru®;Seq RNA Library Preparation Kit v2(Illumina), and RNA sequencing was performed with Illumina Hiseq 2500 at Shanghai Personal Biotechnology Co., Ltd. During the sequencing process, SeqPrep was used to remove splices or merge overlapping paired reads into a single read (https://github.com/jstjohn/SeqPrep), and use Sickle to remove low-quality reads (https://github.com/najoshi/sickle). Then, the data were calibrated with the reference genome of rice (Nipponbare Reference IRGSP-1.0) using HISAT2 v2.1.0. FPKM (Fragments Per Kilobase Millon Mapped Reads) to assess gene expression levels. DESeq2 v1.6.3 is used for differential gene expression analysis between two samples, with q ≤ 0.05 and | log2... | ≥ 1 gene identified as a differentially expressed gene. Through hypergeometric testing, the enrichment in functional terms (GO: terms) was achieved (http://geneontology.org/). Q < 0.05 indicates significant enrichment.
. Results
Polyploidization improves plant height and yield of rice
Polyploidization not only increases the genome capacity and expands the range of genetic variation but also typically increases yield, making it an important application in crop breeding (Cai et al., 2007; Comai, 2005; Koide et al., 2020; Sattler et al., 2016). Previously, we successfully constructed a ‘Balilla’ tetraploid (‘Balilla-4x’) (W. Wang et al., 2022b), and here we first analyzed the agronomic traits of ‘Balilla-2x and 4x’ (i.e., plant height, panicle length, tillering and 1,000-grain weight). The results showed that compared to ‘Balilla-2x’, the plant height of ‘Balilla-4x’ was significantly higher, increasing by 19.35% (Figure 1A–B, Table 1). ‘Balilla-4x’ had longer panicles and thicker stems, with an increase of about 24.58% in panicle length, although the differences in tiller numbers were not significant (Figure 1C–D, Table 1). The grain numbers per panicle of ‘Balilla-4x’ transgenic plants were also obviously higher compared with ‘Balilla-2x’ plants, which increased by 37.60% (Figure 1E, Table 1). The 1,000-grain weight of ‘Balilla-4x’ increased by 33.38% compared to that of ‘Balilla-2x’ (Figure 1F, Table 1). The yield per plant of ‘Balilla-4x’ plants increased by 25.10% (Figure 1G, Table 1). These results indicated that compared to diploid rice, polyploid rice shows a marked potential to increase yield.
Figure 1
Phenotypic characteristics of ‘Balilla-4x’ plants. (A–B) Plant height and phenotypes of ‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’ plants; (C–D) Panicle length; (E) Grains per panicle; (F) 1,000-grain weight; (G) Yield per plant. Data represent means ± SE (n = 10), **P < 0.01, Student’s t-test.
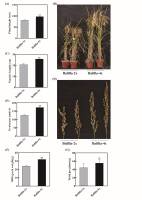
Table 1
Phenotypic data for Balilla-2x and Balilla-4x plants.
Polyploidization changes the grain shape and nutritional quality of rice
In order to determine whether polyploidization affects rice grain shape, we investigated the grain length, grain width and grain thickness of ‘Balilla-4x’. The result indicated that the grain length of ‘Balilla-4x’ plants was higher, increasing by 9.43% compared with that of ‘Balilla-2x’ plants (Figure 2A–B, Table 2). The grain width of ‘Balilla-4x’ plants increased by 12.90% compared with that of ‘Balilla-2x’ (Figure 2C–E, Table 2). The grain thickness of ‘Balilla-4x’ plants increased by 15% compared with that of ‘Balilla-2x’ (Figure 2D, Table 2). These results indicate that the polyploidization of ‘Balilla’ indeed has an impact on the grain shape of rice.
Figure 2
Grain shape features of ‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’. (A–B) Grain length; (C–E) Grain width; (D) Grain thickness; (F) Protein content; (G) Lipid content; (H) Grains phenotypes of ‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’ plants, Bar = 5 mm. Data represents means ± SE, n = 10, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Student’s t-test.
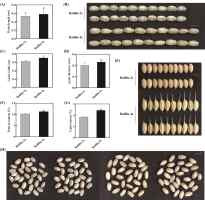
Table 2
Grain shape and nutritional quality data.
Some studies have shown that polyploidization of rice can not only produce beneficial agronomic traits but also improve the nutritional quality of rice (Dhawan & Lavania, 1996; W. Wang et al., 2022b; H. Y. Zhang et al., 2016). Therefore, we tested the nutritional composition of ‘Balilla-4x’. The results showed that compared to ‘Balilla-2x’, ‘Balilla-4x’ plants had increased grain protein content by 10.10% and significantly increased lipid content by 32.07% (Figure 2F–G, Table 2). These results indicate that the polyploidization of ‘Balilla’ not only affects the grain shape of rice but also indeed affects the nutritional quality of rice seed.
Identification of potential target genes affecting plant height and yield of rice
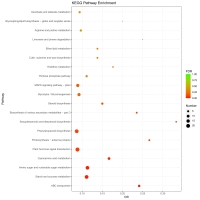
To determine whether the molecular mechanism underlying rice polyploidization affects plant height and yield, gene expression in ‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’ plants was analyzed using high throughput sequencing (HTS). The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the ‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’ plants were further analyzed. The results showed that there were 1,644 upregulated genes (fold change ≥ 2.0) and 1,175 downregulated genes (fold change ≤ 0.5) in ‘Balilla-4x’ plants compared with ‘Balilla-2x’ plants (Table S1, Table 3). The DEGs that affected rice yield were selected by searching the previous reports of characterizing the function of these DEGs. Approximately 10% of the up-regulated DEGs in ‘Balilla-4x’ plants were related to agronomic traits, including plant height, panicle length and yield in rice (Figure 3A). The enriched upregulated genes in ‘Balilla-4x’ plants mainly belong to the following biological process categories: plasma membrane, external encapsulating structure, hydrolase activity or acting on acid anhydrides, lipid metabolic process and cellular response to stimulus (Figure 3B). KEGG metabolic pathway enrichment analysis indicated that DEGs in Ballilla-4x plants do indeed affect these metabolic pathways, such as starch and sucrose metabolism, amino and nucleotide sugar metabolism and plant hormone signal transduction (Figure 4).
Table 3
Partial up-regulated and down-regulated genes from RNA-seq.
| No. | Locus ID | Function | Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LOC_Os06g38120 | Low-affinity cation transporter | 2842.15 |
| 2 | LOC_Os09g36680 | S-like Ribonuclease; S-like RNase | 1254.61 |
| 3 | LOC_Os01g57310 | Magnaporthe grisea resistance-37 | 164.07 |
| 4 | LOC_Os05g39540 | ZRT- and IRT-like protein; metal cation transporter | 157.47 |
| 5 | LOC_Os11g44960 | NBS-LRR disease resistance protein, putative, expressed | 90.94 |
| 6 | LOC_Os10g40720 | β-expansin | 42.28 |
| 7 | LOC_Os01g72370 | bHLH protein | 35.51 |
| 8 | LOC_Os05g12040 | Obtusifoliol 14α-demethylase | 31.17 |
| 9 | LOC_Os07g04020 | EPF/EPFL family gene | 9.43 |
| 10 | LOC_Os03g63970 | Gibberellin 20-oxidase gene; Grain Number per Panicle1 | 5.09 |
| 11 | LOC_Os09g19400 | Carbohydrate-binding malectin-like protein | 0.00 |
| 12 | LOC_Os07g04560 | NAC transcription factor | 0.02 |
| 13 | LOC_Os06g06750 | SEPALLATA-like MADSbox gene | 0.03 |
| 14 | LOC_Os11g38040 | Bright-green leaf | 0.06 |
| 15 | LOC_Os09g36200 | Stay green gene; chlorophyll-degrading Mg++-dechelatase | 0.09 |
| 16 | LOC_Os12g04980 | Homologous pairing aberration in rice meiosis | 0.11 |
| 17 | LOC_Os07g48630 | Rice ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-LIKE gene | 0.50 |
| 18 | LOC_Os03g21030 | NAC (NAM, ATAF, and CUC2) transcription factor | 0.50 |
| 19 | LOC_Os07g05360 | 10 kDa Photosystem II polypeptide | 0.50 |
| 20 | LOC_Os10g29470 | Cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase 3 | 0.50 |
Figure 3
Transcriptome analysis of ‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’ plants. (A) Classification of upregulated genes in ‘Balilla-4x’ plants; (B) Functional enrichment of DEGs in ‘Balilla-4x’ vs. ‘Balilla-2x’ plants. The numbers indicate the gene counts for each functional category.
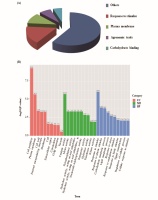
Figure 4
KEGG Pathway functional enrichment of DEGs in ‘Balilla-4x’ vs. ‘Balilla-2x’ plants. The x-axis represents the enrichment factor. The y-axis shows the pathway names. A larger value of the rich factor indicates a higher enrichment value. The color indicates the P value. Point size indicates DEG number, and larger dots refer to higher numbers of DEGs.
Furthermore, we selected several genes related to rice agronomic traits among the DEGs and detected the expression levels of several DEGs through qPCR. The results confirmed that the expression of most selected DEGs (e.g., LOC_Os03g57240, LOC_Os03g03660, and LOC_Os03g63970) was higher in the ‘Balilla-4x’ line than in the ‘Balilla-2x’ line (Figure 5). These results demonstrate that polyploidization can improve rice plant height, and yield may be partially attributed to the regulation of these DEGs. For example, LOC_Os03g57240 (DST) plays a vital role in improving rice grain yield. LOC_Os03g03660 (OsCDPK1) affects plant height and grain size. LOC_Os03g63970 (OsGA20ox1) affects the number of grains per spike. Some of the other DEGs also are involved in regulating rice yield traits. For example, LOC_Os05g32270 (SMOS1) affects organ size. LOC_Os06g10880 (OsbZIP46), LOC_Os07g04020 (OsEPFL5), LOC_Os07g12590 (OsFBX225), LOC_Os07g41200 (GL7), LOC_Os07g46790 (OsDPE2) and LOC_Os11g14220 (OsTubA2) participated in regulating the morphogenesis of rice panicles and affect rice yield. LOC_Os09g29130 (OsZHD1), zinc finger transcription factor, affects internode length, panicle, tiller number and cell size. LOC_Os10g42110 (OsBSK2), a BR signaling pathway kinase, affects grain length and width. LOC_Os01g69830 (qHd1) encodes one gene that affects heading date. LOC_Os02g13900 (OsBZR4) is a member of the BR main signaling pathway, which has a significant impact on many traits of rice plant architecture, grain shape and stress resistance. LOC_Os02g13950 (FUWA) has an impact on rice panicle type, grain type and grain weight. LOC_Os02g42280 (OsGRF4) affects rice grain type and weight. These results demonstrate that many yield-related genes were differentially expressed in the ‘Balilla-4x’ compared with the ‘Balilla-2x’ line and partially explained the increased yield traits in the tetraploid rice (Table 4).
Figure 5
Detection of the relative expression levels of DEGs related to agronomic traits in ‘Balilla-4x’ and ‘Balilla-2x’ plants through qPCR. Data represent means ± SE (n = 3).
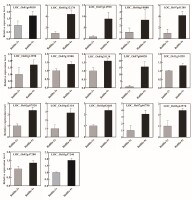
Table 4
Partial DEGs related to plant height and yield.
. Discussion
Polyploid individuals are those with three or more sets of chromosomes in somatic cells. Polyploidization is an important way for many plants and animals to evolve (Jiao et al., 2011; Ni et al., 2009). Many organisms have experienced at least one polyploidization event in their evolutionary history (Jiao et al., 2011; Zhao et al., 2021). Polyploidization typically enables organisms to exhibit strong vitality and adaptability, as well as to adapt to drought, salinity and other stresses (Liu et al., 2023). Therefore, polyploid technology has been applied extensively in plant breeding, especially for important crops such as rice, wheat and soybean (Sun et al., 2020; L. Wang et al., 2021b; N. Wang et al.,2022a). As polyploidization always leads to a reduced seed setting rate, many previous reports on crop polyploidization focused on anther and pollen development (Ku et al., 2022; X. Li et al., 2018). Other studies also indicated that polyploidization affects stomatal morphology, a photosynthetic character of the leaf (Xiong et al., 2022). Compared to its diploid counterpart (‘Balilla-2x’), ‘Balilla-4x’ exhibited increased plant height, panicle length, grain number per panicle and length, width and thickness of rice grains, which contributed to the enhancement of rice yield (Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1). These findings are similar to those of previous studies that reported longer grains and increased biomass yield in autotetraploid rice varieties compared with diploid varieties (Y. C. Li & Rutger, 2007; Tu et al., 2003). In addition, studies have shown that polyploidization leads to changes not only in plant agronomic characters but also in their seed nutrition (Gan et al., 2021; Sattler et al., 2016). We found that compared to diploids, both the protein and the lipid content in tetraploids were increased (Figure 2F–G, Table 2). Our results further support the conclusion that autotetraploid rice is considered better with respect to protein content as compared with diploid rice (Tu et al., 2003), and it will be valuable to cultivate functional rice varieties with a high content of proteins and lipids through polyploidization.
Currently, research on polyploidization is mostly focused on the phenotypic and nutritional composition of plants (W. Wang et al., 2022b; Yuan et al., 2021). However, the mechanism underlying the improvement of crop yield traits by polyploidization is still unclear, especially in rice. Previous studies have conducted several transcriptome and gene expression analyses on polyploid crops. However, most of these studies focused on pollen development and abiotic stress response (Guo et al., 2017; X. Li et al., 2018; N. Wang et al., 2022a; J. Wu et al., 2020). Few reports have studied the molecular mechanism of increased yield traits in polyploid rice. Here, we conducted transcriptome sequencing analysis on ‘Balilla-2x’ and ‘Balilla-4x’ to explore related genes that affect rice agronomic traits. We found that several yield-related genes were up-regulated in ‘Balilla-4x’, such as the GA20 oxidase gene OsGA20ox1, EPF/EPFL family gene OsEPFL5 and zinc finger transcription factor DST, whereas some genes, such as the lipid acid hydrolase gene STH1, were downregulated in ‘Balilla-4x’. OsGA20ox1 is one of the major cloned QTLs controlling rice yield. It encodes a GA20 oxidase that increases cytokinin activity in the rice panicle meristem, thereby increasing grain number and yield (Y. Wu et al., 2016). OsEPFL5 is an EPF/EPFL family gene that positively regulates rice panicle morphogenesis (Guo et al., 2023). DST encodes a zinc finger transcription factor, and its semi-dominant allele DSTreg1 disrupts the regulation of OsCKX2 expression by DST and increases the content of cytokinin in SAM during the reproductive period, resulting in an increase in meristem activity and the number of grains (S. Li et al., 2013). These findings suggest that changes in polyploidized rice agronomic traits may be caused by regulation of the expression of yield-related genes. STH1 encodes one α/β Hydrolase Folding Domain and can play the role of transcription coactivator of zinc finger protein Hd1, regulate the expression level of the florigen gene Hd3a and negatively affect the head time and yield of rice. The translation of STH1 in the African rice variant form was terminated prematurely, and enzyme activity was lost, and introducing this allele caused a significant increase in the number of grains per panicle and the number of branches (Xiang et al., 2022).
Though few studies on the transcriptome supplied information on differentially expressed genes associated with yield traits, TRAQ-based quantitative glutelin proteomic analysis was conducted to supply valuable information on differentially expressed proteins associated with the increased yield of autotetraploid rice. It was revealed that ribosomal proteins and the biosynthesis and metabolism of amino acids were significantly higher in AJNT-4x than in AJNT-2x during endosperm development (Xian et al., 2021). In this study, we also found that amino acids were enriched in the DEGs KEGG analysis. Moreover, our results of GO and KEGG enrichment indicated that sugar metabolism was enhanced in the tetraploid rice. Our results, together with previous reports suggest that the changes in hormone, protein and sugar synthesis and metabolism synergistically altered the agronomic and yield traits of autotetraploid rice.
The mechanism emphasizes that the altered expression of polyploid genes may be related to chromosome structure and epigenetic modifications (Song & Chen, 2015; H. Zhang et al., 2019). Several studies have demonstrated that methylation in many chromosome regions was altered in the autotetraploid rice and thus led to changes in gene expression (Rao et al., 2023; L. Wang et al., 2021a; J. Zhang et al., 2015). For example, it was found that polyploidy induces DNA hypomethylation and potentiates genomic loci coexistent with many stress-responsive genes, which contribute to the increased salt tolerance of tetraploid rice (L. Wang et al., 2021a). It would be valuable to perform the combination analysis of the transcriptome and the methylome of autotetraploid rice, which will imply the molecular mechanism of improved yield traits of polyploidization.
. Conclusion
Tetraploid rice ‘Balilla-4x’ increased plant height, seed number per panicle and yield. The expression of many yield genes (e.g. OsDEP1) was upregulated and that of some genes (e.g. OsEPFL5) was down-regulated, which resulted in the enhancement of sugar and amino acid synthesis and led to an improved yield and quality of rice seeds after polyploidization. This high-yield and nutritious tetraploid strain would be valuable for cultivating novel high-yield and nutrient-rich varieties in future rice breeding.
. Supplementary material
The following supplementary material is available for this article:
Table S1. DEGs that were up-regulated (red) in ‘Balilla-4x’ while down-regulated (green) in ‘Balilla-2x’ are selected for ‘Balilla’ targets.
Table S2. List of primers used in this study.


