. Introduction
The genus Myosotis L. (Boraginaceae) comprises approximately 100 species growing in two main different centers: Eurasia and New Zealand (Chacón et al., 2016; Luebert et al., 2016). Myosotis scorpioides L. grows in the wild across Europe and in some areas of Asia (Siberia, Mongolia, the Caucasus) (Germplasm Resources Information Network [GRIN]) In Poland, the species is found across the country (https://www.atlas-roslin.pl/pelna/gatunki/Myosotis_palustris.htm). M. scorpioides plants mostly occur on water banks, wet meadows, thickets, bog springs, and peat bogs (Kłosowski & Kłosowski, 2006; Podbielkowski & Sudnik-Wójcikowska, 2003), where they form large knee-high colonies (Fletcher & Tomblin, 2005). The species prefers moderately sunny locations and wet humus- and nutrient-rich soils (https://www.atlas-roslin.pl/pelna/gatunki/Myosotis_palustris.htm). It is also grown as an ornamental plant (Podbielkowski & Sudnik-Wójcikowska, 2003).
The genus Myosotis belongs to the subfamily Cynoglossoideae and tribe Myosotideae Rchb. (Weigend et al., 2016). M. scorpioides produces light blue flowers with flat-spread corolla lobes. Its buds and young flowers are pink (Podhajská & Rivola, 1992). The plant blooms from May to September. The flowers are entomophilous or self-pollinating (Rutkowski, 2006).
Myosotis pollen is very small and represents the smallest pollen grains known (Stanley & Linskens, 1974). Most Cynoglossoideae, including Myosotis plants, produce heterocolpate pollen characterized by the presence of two alternately arranged types of apertures: true apertures (colpori) and pseudoapertures (pseudocolpi) (Hargrove & Simpson, 2003; Weigend et al., 2016). It has been shown that heterocolpate pollen grains are not found in the other Boraginaceae subfamilies (Díez & Valdés, 1991).
The morphology of pollen grains in the genus Myosotis is highly diverse (Beug, 2004; Meudt, 2016). Large differences have been found in their size and shape and in the number of apertures (Díez & Valdés, 1991; Noroozi et al., 2022).
The morphology and ultrastructure of the sporoderm of Myosotis palustris pollen grains have been thoroughly investigated by Volkova et al. (2013). The development and structure of pollen grains in M. azorica and M. laxa growing in Argentina were presented by Strittmatter and Galati (2001). Meudt (2016) carried out comparative studies of the morphology of pollen grains in 30 different taxa of Myosotis growing in New Zealand. The development of the sporoderm in M. scorpioides was studied in Russia by Volkova et al. (2017). There is no sufficient data in the literature regarding the ultrastructure of the cytoplasm in Myosotis pollen grains.
The aim of the study was to analyze the structure of the anther wall, identify the tapetum type, and examine the size and subcellular aspects of M. scorpioides pollen grains, as there are no data on this issue in the available literature.
. Materials and methods
Plant material
The samples were collected from Myosotis scorpioides L. plants growing in their natural localities in Krężnica Jara (51°09′04″ N, 22°28′52″ E) in 2022–2023. The botanical identification of the specimens was carried out by taxonomy specialist Professor Bożena Denisow. The plant specimens were also compared with samples (voucher specimen no. 152) deposited in the herbarium of the Department of Botany and Plant Physiology, University of Life Sciences in Lublin (Poland).
Pollen grain size – Light microscopy (LM) studies
Glycerine jelly preparations of pollen grains were made, and the length of their polar (P) and equatorial (E) axes was measured (n = 50) with the use of a Nikon Eclipse 400 light microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
Morphology of pollen grains – Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) studies
To examine the pollen morphology using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), pollen grains were collected from the flowers on flowering days 1–2. The methodology was based on a simplified microscopic preparatory approach. The pollen grains were placed on the surface of stubs covered with carbon tape and sputtered with gold using an Emitech SC 7640 sputter coater (Polaron, Newhaven, East Sussex, the UK). The observations of the shape and surface of the pollen grains and the documentation were made using a TESCAN/VEGA LMU (Tescan, Brno, the Czech Republic) scanning electron microscope (an accelerating voltage of 30 kV) equipped with a TESCAN attachment for digital processing of microscopic images.
Ultrastructure of pollen grains - Transmission electron microscope (TEM) studies
The pollen grains were fixed in 4% glutaraldehyde in phosphate buffer (pH 7.2; 0.1 M) at 4 °C for 12 h, washed three times in phosphate buffer, and dehydrated in an ethanol series. The samples were post-fixed in a 1% osmium tetroxide solution at 0 °C for 1.5 h and washed three times in distilled water. In the next step, they were dehydrated in a graded ethanol series and embedded in LR white resin (LR white acrylic resin, medium grade, Sigma-Aldrich). Following polymerization at 60 °C, ultrathin sections (60–70 nm) of the embedded material were obtained for TEM examinations (copper grids with a 300 square mesh were used) using a Reichert Ultracut S ultramicrotome and a glass knife. Finally, the pollen grains were stained with 0.5% uranyl acetate and post-stained with 0.5% lead citrate (Reynolds, 1963). The ultrastructure of the pollen grains was analyzed with the use of a JEM 1400 (JEOL Cp., Japan) transmission electron microscope at an accelerating voltage of 120 kV. Photographic documentation was made using an 11 Magapixel TEM Camera MORADA G2 (EMSIS GmbH, Münster, Germany).
The diameter of plastids and mitochondria (n = 20 each) and the height of orbicules (n = 20) were measured (5 samples).
. Results
Anther structure
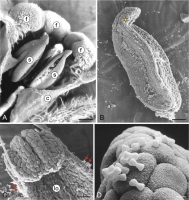
M. scorpioides produces actinomorphic gamopetalous flowers. Their equally sized stamens (5) are fused with the upper part of the corolla tube (Figure 1A). The length of the anther is 0.7–0.9 mm (0.8 µm ± 0.08; mean ± SD), and its diameter at the widest point is 0.3–0.4 mm (0.37 µm ± 0.04; mean ± SD). The apical part of the anther ends with a slightly centrifugally bent appendix (Figure 1A–B). The anthers are latrorse and dehisce by means of a longitudinal slit (Figure 1A). The pollen grains are much smaller than the anther epidermis cells (Figure 1C–D). The surface of the epidermis cells is covered by a cuticle with characteristic ornamentation (Figure 1D).
Figure 1
Fragments of Myosotis scorpioides L. flowers and stamens (SEM). Upper part of the flower with visible fornices and stamens fused with the corolla tube (A); anther in a lateral position; centrifugally bent connective process in the apical part (yellow asterisk) (B); fragment of a mature anther after the release of pollen grains (red arrows) with a visible loculus (C); anther surface with visible cuticle ornamentation on the outer wall of epidermis cells and mature pollen grains (D). c – corolla tube; f – fornices; lo – loculus; s – stamens. Scale bars: (A) = 200 µm, (B) = 100 µm, (C) = 20 µm, (D) = 5 µm.
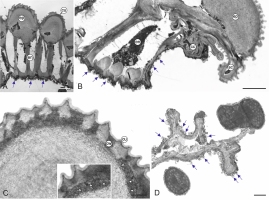
The cross-section of the anther wall shows three layers: a one-layered epidermis covered by cuticle, the endothecium with large cells with bar thickenings, and the remains of the middle layer and tapetum tangential walls (Figure 2A). The size of the epidermis cells in the stomium region is substantially smaller than the other cells of this tissue (Figure 2B). In the outer wall of the epidermis cells, there are electron-translucent and electron-dense zones with numerous small droplets (Figure 2C), whose presence may indicate the secretory properties of this tissue.
Figure 2
Ultrastructure of M. scorpioides L. anther wall (TEM). Cross-section of an anther wall with a visible epidermis layer, endothecium with fibrous bands, remains of middle layer (red asterisks), and orbicules (blue arrows) on the surface of tapetum tangential walls (A); anther wall cells located adjacent to the stomium: epidermis, small stomium epidermis cell, endothecium, orbicules (blue arrows), and crushed cells during stomium rupture (B); fragment of an epidermal cell with cell wall details: cuticle, cell wall with zones of electron-dense, electron-transparent, and small droplets (white arrows) (C); deformed cells forming the septum between the loculi after anther rupture; blue arrows indicate orbicules (D). cc – crushed cells; cu – cuticle; cw – cell wall; en – endothecium; ep – epidermis; sc – stomium cells. Scale bars: (A–B) = 5 µm, (D) = 2 µm, (C) = 1 µm.
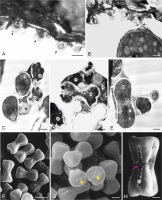
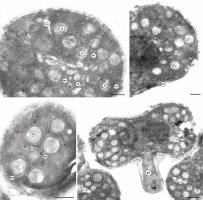
The inner surface of the anther wall is covered by orbicules (Figure 2A–B). They are also present on the walls of the endothecium radial walls (Figure 2B) and on the surface of cells forming a septum between the loculi. It seems that the orbicules are associated with the tapetum cell remains present on the inner locule surface (as seen in Figure 3A–B) (Figure 2D). The orbicules are polygon-like in cross-section with an electron-opaque cavity and an electron-translucent orbicule wall (Figure 3A–B). Their size is in the range of 0.42–0.67 µm (0.55 µm ± 0.07 on average). In some areas, the orbicules and the pollen grain sporoderm are fused (Figure 3B). Plasmodial tapetum protoplasts are visible from the microspore stage to the 3-celled microgametophyte stage; they surround the pollen grains, forming a periplasmodium layer (Figure 3C–E).
Figure 3
Inner part of the M. scorpioides L. anther wall surrounding the loculus, pollen grains, and plasmodial tapetum in the 3-celled pollen grain phase (TEM) (A–D). Heterocolpate pollen grains of M. scorpioides L. viewed in the scanning electron microscope (SEM) (F–H). Remains of tapetum cell walls and deformed cells of the intermediate layer and orbicules (blue arrows) (A); orbicules fused with the pollen grain wall (black arrows) (B); plasmodial tapetum protoplasts located in close proximity to pollen grains (C); pollen grains surrounded by the periplasmodium (D–E); Pollen grains with equatorial constrictions and furrows with various lengths (F); pseudoporus (yellow arrow) with granular exine ornamentation at the poles of the pollen grains (G); pollen grain with a longer pseudocolpus and a short colpus containing a porus (purple arrow); granular exine ornamentation on the edges of the furrows (H). pg – pollen grains; pt – plasmodial tapetum; pp – periplasmodium; ps – pseudocolpus; sc – short colpus. Scale bars: (D, G) = 2 µm, (C, E, H) = 1 µm, (A, B) = 0.5 µm.
Pollen grain morphology
M. scorpioides pollen grains are very small and dumbbell-shaped with a constriction in the equatorial plane (Figure 3F). The average length of the polar axis (P) is 7.5 µm (±0.16), the length of the equatorial diameter (E) is 3.2 µm (±0.20), and the diameter of the pollen grain at the widest point of the pole is 4.5 µm (±0.15). The grains are heterocolpate with three pseudocolpi and three alternately arranged colpori (Figure 3F). The pores are fused with colpi and located in the equatorial plane. Given the number and type of apertures, M. scorpioides pollen grains are classified as tricolporate. The structure of their poles allows the classification of the grains as isopolar and subhexagonal in the polar view. At each pole, there is a pseudoaperture with granular ornamentation (Figure 3G). The exine ornamentation in the intercolpi is psilate, while the margins of the colpi are granular (Figure 3H).
Ultrastructure of pollen grains
The ectexine and endexine in the intercolpi are very thin, whereas the endexine near the endoaperture is thick (Figure 4A). The intine is thick only on the endoaperture. Pollenkit is visible on the exine surface and among the bacula (Figure 4B). Mature pollen grains are 3-celled (Figure 4A–C). Two sperm cells are enclosed in the vegetative cell. The sperm cell has a very small amount of cytoplasm. The nuclei of the sperm cells are slightly lobulated and unilaterally flattened (Figure 4C–D). Many organelles are situated in the cytoplasm of the vegetative cell, which has a highly lobulated nucleus (Figure 4C–E). In the polar regions, there are plastids surrounded by rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) profiles (Figure 5A–C). The size of the plastids is in the range of 0.38–0.50 µm (0.43 µm ± 0.05 on average). The plastids contain tubule-like thylakoids (Figure 5A–C). Very numerous ribosomes and RER profiles are present in the entire vegetative cell (Figure 4C–D, Figure 5C). Mitochondria, circular in cross-section, are concentrated in the equatorial region of the pollen grains (Figure 4A, Figure 4D–E). Their diameter is in the range of 0.19–0.20 µm (0.19 µm ± 0.01 on average). Numerous different-sized vesicles are visible in the cytoplasm (Figure 4D, Figure 5A). The pollen grains germinate through colpori (Figure 5D).
Figure 4
Ultrastructure of M. scorpioides L. pollen grains (TEM). Longitudinal section of a pollen grain (A); fragment of a pollen grain with visible sporoderm and pollenkitt (green arrow) (B); submedial parts of protoplasts with sperm cells, plastids, numerous mitochondria, vesicles, RER profiles, and very numerous ribosomes (arrowheads) (C–D); lobulated vegetative nucleus with a nucleolus, sperm cells, numerous mitochondria, and plastids (E). mc –sperm cells; m – mitochondria; nu – nucleolus; pl – plastids; rer – rough endoplasmic reticulum; ve – vesicles; vn – vegetative nucleus. Scale bars: (A) = 1 µm, (B–E) = 0.5 µm.
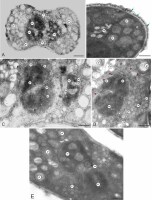
Figure 5
Fragments of the longitudinal section (a, b) and cross-section (c) of M. scorpioides L. pollen grains and a pollen grain with a germinating pollen tube (d) (TEM). Numerous circular plastids with thylakoids surrounded by RER profiles, vesicles, RER profiles, very numerous ribosomes (arrowheads) (A–C); pollen tube germinating from the equatorial part of the pollen grain (D). pl – plastids; pt – pollen tube; rer – rough endoplasmic reticulum; ve – vesicles. Scale bars: (D) = 1 µm, (A–C) = 0.5 µm.
. Discussion
The current study presents details of the structure of the mature anther wall in M. scorpioides, including details of the stomium and identification of the tapetum type. At this stage of development, the anther loculus was surrounded only by the epidermis and the endothecium, as well as the remains of the middle layer and tapetum cell walls, with orbicules visible on their surface. The parietal layers between the endothecium and the tapetum were crushed and collapsed. Similar changes in mature anthers were highlighted by Esau (1973). Secondary thickening of endothecium cell walls was visible as ledges both on the internal tangential walls and on the radial walls. Garcia (2002) distinguished four main types of endothecial secondary thickening: (1) annual rib type, (2) helical rib type, (3) reticulate ribs, and (4) palmate ribs. The present observations suggest that the thickening in the M. scorpioides endothecium can be classified as the annual rib type.
We observed that the stomium region of the dehiscent M. scorpioides anthers after pollen release exhibited the presence of well-preserved small epidermis cells, which are typical of this part of the anther. Close to these cells, there were crushed and deformed septum cells that previously separated the two loculi. As reported by Wilson et al. (2011), the septum in the mature anther is enzymatically lysed and undergoes a programmed cell death-like breakdown. In turn, the stomium rupture is a consequence of stresses associated with pollen swelling and anther dehydration. Ligno-cellulosic secondary thickening in endothecium walls, which is well formed in M. scorpioides anthers, also plays an important role in the opening of anthers.
The present study shows that M. scorpioides has a plasmodial tapetum, characterized by the release of tapetum cell protoplasts from cell walls and their penetration into the loculus, where they surround and nourish the forming pollen grains. The protoplasts fuse to form a multinucleate periplasmodium (Furness, 2008; Pacini, 1996). During the development of pollen grains, plasmodia gradually disappear (Esau, 1973). Other authors have reported the presence of a secretory tapetum in most Boraginaceae representatives (Izmaiłow & Biskup, 2003; Johri et al., 1992; Rao & Rao, 1992). The secretory tapetum is predominant in angiosperms (Furness & Rudall, 2001; Pacini et al., 1985). In this tapetum type, a layer of tapetal cells surrounds the anther loculus. In previous studies, the tapetum in Myosotis azorica, M. laxa (Strittmatter & Galati, 2001), and M. scorpioides (Volkova et al., 2017) was classified as the secretory type. A secretory tapetum was also identified in Symphytum orientale (Boraginaceae) (Vardar & Yavuz, 2018), whereas two types of tapetum, i.e. secretory and plasmodial, were present in Symphytum officinale(Gabarayeva et al., 2011). It seems that M. scorpioides may be characterized by the occurrence of different types of tapetum, i.e., secretory and plasmodial.
In the present study, the tapetum penetrated the anther loculus at the microspore stage and remained there until the later stage of pollen development. Similar observations of the functioning of the plasmodial tapetum in Butomus (Butomaceae) were reported by Fernando and Cass (1994). Plasmodial tapetum has also been described in many other Eudicots. In Asteraceae (e.g. Helianthus annus) (Çetinbaş & Ünal, 2015) and Caprifoliaceae, plasmodial tapeta predominate (Furness, 2008; Pacini, 1996). This tapetum type has also been found in, e.g., Apiaceae, Berberidaceae, Gentianaceae, Oleaceae, Verbenaceae (Furness, 2008), and Alismataceae (Hydrocleys nymphoides, Alisma plantago-aquatica, and Sagittaria montevidensis) (Nicolau et al., 2024).
In the M. scorpioides anthers, polygonal-shaped orbicules were observed on the surface of the tapetum cell remains and on the surface of the pollen grains. This morphological type of orbicules occurs in a few plant species, e.g., in some Piperales (Oak et al., 2022). Most often, orbicules have a spherical or nearly spherical shape (Ruggiero & Bedini, 2020; Vinckier & Smets, 2002a, 2002b). To date, great diversity in the shape, size, density, and ornamentation of orbicules has been observed in different families (Galati, 2003; Oak et al., 2022; Ruggiero & Bedini, 2018, 2020; Verstraete et al., 2014). Orbicules are sporopollenin particles involved in the formation of the sporoderm of pollen grains (Huysmans et al., 1998). The fusion of the orbicules with the cell wall of pollen grains in the anthers of M. scorpioides, which was shown in the present study by transmission electron microscopy, may confirm this information.
As shown by literature data, orbicules occur mainly in anthers that contain a secretory tapetum (Huysmans et al., 1998; Verstraete et al., 2014; Vinckier & Smets, 2003). Therefore, it may be assumed that the occurrence of orbicules in M. scorpioides anther loculi where the plasmodial tapetum was present is an exception. The unique species in this respect reported previously included Gentiana acaulis L. (Lombardo & Carraro, 1976; Vinckier & Smets, 2002a; 2002b) and Tradescantia virginiana (Tiwari & Gunning, 1986), in which orbicules were accompanied by a plasmodial tapetum as well. Galati et al. (2007) reported the presence of orbicules in the anthers of Modiolastrum malvifolium (Malvaceae), which had an invasive non-syncytial tapetum classified as intermediate between secretory and plasmodial tapetum. The authors found that the presence of orbicules is not associated with the tapetum type, as they occur in both the secretory and plasmodial tapetum.
The shape of the polygonal orbicules present in the M. scorpioides studied differed from the shape of orbicules found in other Myosotis species. Strittmatter and Galati (2001) reported the presence of spherical and subspherical orbicules in M. azorica and M. laxa. These data indicate diversity in the morphology of orbicules in different species of the genus.
The size of the orbicules in M. scorpioides was in the range of 0.42–0.67 µm, i.e. they can be classified as small in comparison with other literature data. Vinckier and Smets (2003) reported the size of orbicules in representatives of the family Gentianaceae in the range of 0.14–2.98 µm. As shown by Ruggiero and Bedini (2020), the size of orbicules in 34 species from different families ranged from 0.06 to 2.56 µm. In turn, Oak et al. (2022) reported a range of 0.24–2.79 µm in 12 Piperales species. As reported by Ruggiero and Bedini (2020), there is an evolutionary trend towards a reduction in the size of orbicules in angiosperms. Tiwari and Gunning (1986) found that orbicules in anthers with ameboid tapeta are smaller than in secretory tapeta.
The present study indicated the presence of three cells in mature pollen grains in M. scorpioides: a vegetative cell and two sperm cells located therein. Similarly, 3-celled pollen grains were described in M. azorica and M. laxa by Strittmatter and Galati (2001). In their study on the development of pollen grains in M. scorpioides, Volkova et al. (2017) carried out a detailed analysis of the development of the sporoderm in this species, but without information on the internal structure of pollen grains.
The analyses of the ultrastructure of M. scorpioides pollen grains revealed the presence of slightly lobulated nuclei and small amounts of cytoplasm in the sperm cells. In turn, the nucleus of the vegetative cell was intensively lobulated. The cytoplasm of the vegetative cell contained numerous plastids surrounded by the RER. The plastids had a system of internal membranes. There were also mitochondria, RER profiles, very numerous ribosomes, and different-sized vesicles. Some of these structures, i.e., proplastids, RER profiles, and mitochondria, were observed in the vegetative cells of M. azorica and M. laxa (Strittmatter & Galati, 2001). Noteworthy are the exceptionally small sizes of plastids (0.38–0.50 µm) in the M. scorpioides pollen grains. Fujiwara et al. (2010) described plastids in pollen grains and growing tubes from transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana reaching a length of 0.3–3.1 µm (1.4 ± 0.4 µm on average). In turn, plastids with a diameter of 4–6 µm were found in somatic cells of angiosperms (Evert, 2006). Boussardon et al. (2023) described plastids in mesophyll cells reaching a diameter of ca. 5–8 µm, while plastids in phloem cells were smaller (ca. 3–6 µm). The mitochondria in the M. scorpioides pollen grains analyzed in the present study were small (0.19–0.20 µm). Similarly, Liu (2012) reported that the diameter of mitochondria in spindle-shaped generative cells of Citrullus lanatus cv. Jinzhongguanlong was ca. 0.16 µm, while in the newly born generative cells reached ca. 0.5 µm. In turn, mitochondria in plant cells were shown to have a length of 1–3 µm and an approximately 0.5 µm diameter (Møller et al., 2021).
The high number of ribosomes present in the M. scorpioides pollen grains indicates the possibility of intensive protein biosynthesis. It has been shown that the formation of polyribosomes and the synthesis of new proteins occurring in pollen grains determine pollen tube growth (Mascarenhas, 1993).
The sperm cells and the vegetative nucleus in M. scorpioides were located in the pollen grains semi-medially on both sides of the equatorial constriction. A similar arrangement of these structures in pollen grains was observed in M. azorica and M. laxa (Strittmatter & Galati, 2001). Similarly, the same arrangement of sperm cells and the vegetative nucleus in pollen grains were found in Cryptantha intermedia, a representative of Boraginaceae, which has pollen grains of a similar type (Hargrove & Simpson, 2003).
The cross-sections of the pollen sporoderm examined in this study revealed the presence of pollenkitt, which was visible on the surface of the exine and between the bacula. Strittmatter and Galati (2001) also described the presence of pollenkitt on the surface of pollen grains of two other Myosotis species. Pollenkitt is produced by the anther tapetum. One of its many functions is its involvement in nutrition and pollen development (Pacini & Hesse, 2005).
The images of the analyzed pollen grains with the pollen tube prove that the germinative pores were located in the colpori in the equatorial part of the pollen grains. Therefore, the present observations confirm the findings reported by Strittmatter and Galati (2001), showing that colpori serve a functional role in pollen grain germination. The authors also found that, after release from anthers, M. azorica and M. laxa pollen grains are ready for rapid germination. The present observations indicate a similar phenomenon in M. scorpioides.
Another function is played by pseudocolpi, which were arranged alternately with colpori. According to the current knowledge, pseudocolpi in heterocolpate pollen grains perform the function in harmomegathy, which allows controlling the processes of hydration and dehydration. In some Boraginaceae, including Myosotis, the presence of pseudocolpi determines the particular flexibility of the pollen wall (Volkova et al., 2013). Harmomegathy enables pollen grains to adapt to dispersal when they are partially dehydrated and to take up water before they emit pollen tubes. This is possible due to the elasticity of pollen walls provided by the special structure of furrows, which are flexible and facilitate changes in volume (Božič & Šiber, 2020; Katifori et al., 2010; Pacini & Franchi, 1999; Taia, 2022).
. Conclusions
The plasmodial tapetum in M. scorpioides anthers is active in pollen loculi from the microspore phase to the late phase of pollen grain development, as the periplasmodium formed from the protoplasts of tapetum cells surrounds these grains in the 3-celled phase.
The orbicules covering the inner surface of the anther wall have a polygonal shape, which has not often been evidenced in plants so far.
The numerous organelles contained in pollen grains (plastids, mitochondria) are substantially smaller than those contained in plant somatic cells. The abundant distribution of ribosomes in both the central and distal parts of pollen grains indicates the possibility of intensive protein synthesis, which usually accompanies germination and pollen tube growth.


